Abstract
Introduction
Achieving minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity in multiple myeloma (MM) is positively correlated with prolonged PFS and OS (Landgren 2016, Munshi 2017), and longitudinal assessment of MRD can provide additional prognostication (Diamond 2021). This is substantiated by the inclusion of sustained MRD negativity (defined as two consecutive MRD negative results ≥12 months apart at 10 -5 threshold) within IMWG and NCCN guidelines as part of the response criteria for symptomatic MM. MRD has also recently been adopted as a potential primary endpoint in clinical trials, and there is increasing focus on the role of MRD in guiding treatment decisions, including discontinuation of therapy (Lahuerta 2021). Standardized, sensitive, and serial MRD assessment is useful to support both routine patient management consistent with guidelines, and clinical studies which incorporate MRD as a primary endpoint.
NGS MRD (clonoSEQ Assay, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Seattle, WA) is currently the only FDA authorized test available for MRD assessment in patients with MM using bone marrow. The assay's standardization, sensitivity, and wide availability facilitates real-world evidence (RWE) analyses looking at MRD trends in MM patient cohorts over time. The aim of this abstract is to provide further insight into longitudinal MRD testing patterns and attainment of sustained MRD negativity in a real-world cohort of patients.
Methods
The study population includes a de-identified internal dataset of MM samples processed as part of Adaptive's clinical offering (excluding trials) to support routine patient management; patients were geographically dispersed and treated at a variety of institutions, and the analysis period was from January 2018 to July 2021. We examined sustained MRD negativity and other longitudinal patterns of MRD testing and negativity at deep MRD thresholds.
Results
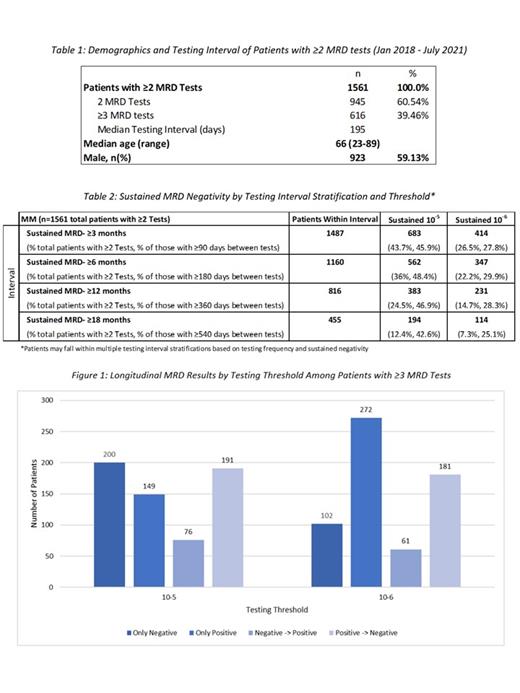
In the analysis period, we identified 1,561 MM patients with at least two MRD tests following a trackable sequence from a baseline clonality (ID) test. Of those patients, 616 had ≥3 tests. The median testing interval for patients with ≥2 MRD tests was 195 days. The median age was 66 and 59% were male, which is generally consistent with epidemiological data.
When examining MRD monitoring longitudinally, of the 1,561 patients that had ≥2 MRD tests, 383 (24.5%) and 231 (14.7%) patients had sustained MRD-negativity for at least 12 months at 10 -5 and 10 -6 thresholds, respectively. Of the 616 patients with ≥3 MRD tests, 200 (32.5%) and 102 (16.6%) has remained negative throughout the testing period, 191 (31.0%) and 181 (29.4%) had converted from positive to negative, and 76 (12.3%) and 61 (9.9%) had converted from negative to a positive state at the respective thresholds. The trends within subgroups (only positive, only negative, negative -> positive, and positive -> negative) vary based on a deeper sensitivity threshold.
Conclusions
Serial measurement of MRD can facilitate a dynamic assessment of risk for disease progression in patients with MM, and this real-world analysis of MRD clinical samples provides insight into serial testing patterns and sustained MRD-negativity using next-generation sequencing.
Jiang: AstraZeneca LLC: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Ended employment in the past 24 months; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Current Employment. Lee: Adaptive Biotechnologies: Current Employment. Eckert: Adaptive Biotechnologies: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Demaree: Adaptive Biotechnologies: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Hewitt: Adaptive Biotechnologies: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal